
Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection

- Key Benefits of Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection
- A Detailed Guide to Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection
- Which software firewall offers optimal threat protection for average users?
- What type of firewall configuration is considered most user-friendly for implementation?
- What is the most straightforward firewall architecture for basic network security?
- To what extent can software firewalls effectively mitigate cybersecurity threats?
- More information of interest
Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection, in today's interconnected digital landscape, robust cybersecurity measures are more critical than ever. Among the most accessible and effective tools for safeguarding personal and business systems are . These applications serve as the first line of defense, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Designed for user-friendly operation, they provide essential barrier functions without requiring advanced technical knowledge. By filtering potential threats and unauthorized access attempts, such firewalls offer a streamlined approach to maintaining digital security, ensuring that users can operate online with confidence and reduced risk.
You may also be interested in reading: Best Firewalls with IDS for Security in 2025
Key Benefits of Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection
Software firewalls operate as applications installed on individual devices, providing a critical layer of security by monitoring and controlling network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Unlike hardware firewalls that protect entire networks, software firewalls offer personalized protection for specific devices, making them particularly valuable for personal computers, laptops, and mobile devices. Their configuration flexibility allows users to create custom rules for different applications and network types, while real-time monitoring capabilities help detect and block suspicious activities before they can cause harm.
Software firewalls prevent unauthorized access by continuously monitoring all incoming and outgoing network traffic. They analyze data packets against a set of security rules, blocking any connection attempts that don't meet the established criteria. Modern firewalls utilize stateful packet inspection to track active connections and make context-aware decisions, while application-layer filtering enables them to control specific program access to network resources. This multi-layered approach ensures comprehensive protection against various cyber threats.
Configuring Your Software Firewall for Optimal Security
Proper configuration is essential for maximizing firewall effectiveness. Users should begin by enabling the firewall's default deny policy, which blocks all traffic except explicitly permitted connections. Creating specific rules for trusted applications, setting up network zone profiles (public, private, domain), and regularly updating the rule set based on current security needs are critical steps. Most modern software firewalls offer intuitive interfaces with guided setup wizards to simplify this process for non-technical users.
Real-Time Monitoring and Threat Detection Features
Advanced software firewalls provide comprehensive real-time monitoring dashboards that display active connections, blocked attempts, and security events. They employ intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to identify and respond to suspicious patterns. Many solutions integrate with threat intelligence feeds to automatically update their protection mechanisms against emerging threats, providing proactive defense without requiring constant user intervention.
Integration with Other Security Solutions
Software firewalls work most effectively when integrated with other security components such as antivirus software, anti-malware tools, and endpoint protection platforms. This integration enables coordinated responses to threats, where the firewall can block malicious traffic while other components handle infected files or compromised applications. Many comprehensive security suites now include firewall functionality as part of their layered defense strategy, ensuring seamless operation between different protective elements.
Choosing the Right Software Firewall Solution
Selecting appropriate software firewall protection requires evaluating several factors including system compatibility, resource usage, ease of use, and feature set. Enterprise solutions typically offer centralized management consoles, while consumer-focused products prioritize simplicity and automation. Considerations should include the firewall's logging capabilities, update frequency, technical support availability, and compliance with relevant security standards for your specific environment.
| Feature | Basic Firewalls | Advanced Solutions |
| Application Control | Limited predefined rules | Customizable per-application settings |
| Network Monitoring | Basic traffic logging | Real-time connection tracking |
| Threat Prevention | Standard packet filtering | Behavior-based detection |
| System Resources | Minimal impact | Moderate to high usage |
| Management Interface | Simple configuration | Detailed advanced controls |
A Detailed Guide to Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection
Which software firewall offers optimal threat protection for average users?

For average users seeking optimal threat protection, Windows Defender Firewall integrated with Windows Security provides comprehensive, user-friendly protection that effectively blocks malicious traffic while maintaining system performance, complemented by built-in antivirus and network monitoring features; third-party options like ZoneAlarm Free Firewall offer additional control with minimal configuration, though most users will find Microsoft's solution sufficiently robust for everyday threats as part of a layered security approach using Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection.
Built-in Windows Defender Firewall Features
Windows Defender Firewall, included with Windows 10 and 11, offers robust outbound and inbound protection with automated rule management, seamlessly integrating with Microsoft Defender Antivirus for real-time scanning; its network profiling (Domain, Private, Public) adapts security levels automatically, while the Windows Security Center provides clear status alerts and simple toggle controls for average users without requiring technical expertise.
Third-Party Firewall Options for Enhanced Control
Third-party firewalls like Comodo Free Firewall and GlassWire provide advanced features such as application behavior monitoring, detailed traffic visualization, and customizable pop-up alerts for connection attempts, giving users finer control over network permissions; these tools often include intrusion detection systems and virtualized environments for suspicious programs, though they may require more user interaction compared to built-in solutions.
Balancing Protection and Usability
Optimal software firewalls for non-technical users prioritize automated decision-making and silent operation, minimizing pop-ups while maintaining strong default-deny policies for unknown applications; key aspects include low system resource usage, clear privacy policies, and regular automatic updates to threat databases, ensuring protection without complicating the user experience.
| Firewall | Key Feature | User Difficulty | Threat Protection Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Defender | OS Integration | Low | High |
| ZoneAlarm Free | Application Control | Medium | High |
| Comodo Firewall | Defense+ Sandbox | High | Very High |
| GlassWire | Traffic Visualization | Medium | Medium-High |
What type of firewall configuration is considered most user-friendly for implementation?
The most user-friendly firewall configuration for implementation is typically a stateful inspection firewall managed through a cloud-based unified threat management (UTM) system with a graphical user interface (GUI), as it combines automated rule sets, intuitive dashboards, and pre-configured security policies that minimize manual configuration while providing robust protection against common threats, including integrated features like intrusion prevention and application control that operate seamlessly without requiring advanced technical knowledge from the user.
Key Features of User-Friendly Firewalls
User-friendly firewalls prioritize features such as automated updates, drag-and-drop rule creation, and real-time alerts that simplify ongoing management. These systems often include preset security profiles for different environments (e.g., home, office, or public Wi-Fi), allowing users to deploy protection quickly without deep expertise. Additionally, integration with centralized management consoles enables consistent policy application across multiple devices, reducing the risk of configuration errors. For example, many modern solutions offer one-click threat mitigation and visual traffic monitors, making it easier to identify and respond to issues.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automated Rule Sets | Reduces manual input and potential errors |
| GUI-Based Controls | Enables intuitive navigation and configuration |
| Pre-Configured Templates | Speeds up deployment for common use cases |
Recommended Firewall Types for Non-Technical Users
For non-technical users, software firewalls integrated into operating systems or offered as standalone applications are highly recommended due to their ease of installation and minimal configuration requirements. Solutions like Windows Defender Firewall or third-party Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection often feature guided setup wizards and default-deny policies that balance security and usability. These firewalls typically run silently in the background with periodic prompts for user decisions, ensuring protection without complex input. Their adaptability to various devices and environments makes them accessible while still providing essential security layers against common cyber threats.
Implementation Best Practices for Simplicity
To ensure a straightforward implementation, start by enabling default firewall settings and using vendor-provided templates that match your network environment (e.g., home, small business). It is crucial to segment networks visually through the firewall’s GUI to apply policies granularly without command-line complexity. Regularly review automated reports and set up scheduled scans to maintain security with minimal effort. Avoiding advanced custom rules unless necessary and relying on built-in threat intelligence feeds can further reduce the administrative burden while keeping defenses strong against evolving risks.
What is the most straightforward firewall architecture for basic network security?
The most straightforward firewall architecture for basic network security is a single-tier or packet-filtering firewall deployed at the network perimeter, typically using a hardware-based appliance or a router with built-in firewall capabilities that inspects incoming and outgoing traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols while employing a default-deny policy that only allows explicitly permitted traffic, providing an essential barrier against unauthorized access without complex configurations.
Core Components of a Basic Firewall Setup
A basic firewall setup consists of key components including a hardware or software device that enforces access control rules between networks, a rule set defining permitted and blocked traffic based on criteria like IP addresses and ports, and a management interface for configuration. This architecture often integrates with a network address translation (NAT) function to mask internal IP addresses and may include logging capabilities to monitor traffic events. For smaller environments, Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection can be deployed directly on endpoints to complement the network firewall, adding a layer of security without significant overhead.
Key Configuration Steps for Implementation
Implementing a straightforward firewall involves defining a default-deny rule as the baseline policy to block all traffic unless explicitly allowed, creating specific permit rules for necessary services such as web browsing (port 80/443) or email (port 25), and regularly reviewing and updating rules to adapt to network changes. It is critical to segment internal networks if possible, disable any unnecessary administrative services on the firewall itself, and ensure that logging is enabled to detect and respond to potential incidents. The following table summarizes essential configuration actions:
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Set default policy to deny all | Block unauthorized traffic by default |
| 2 | Create allow rules for required ports | Permit essential services (e.g., HTTP, DNS) |
| 3 | Enable logging for denied traffic | Monitor and troubleshoot access attempts |
| 4 | Disable unused services on firewall | Reduce attack surface |
Common Use Cases and Limitations
This simple architecture is ideal for small offices or home networks where the primary goal is to block unsolicited inbound traffic and prevent basic threats like port scans or unauthorized access attempts, but it lacks advanced features such as deep packet inspection (DPI) or application-aware filtering,
making it less effective against sophisticated attacks like encrypted threats or application-layer exploits. Additionally, while it provides perimeter security, it does not protect against internal threats or lateral movement within the network, necessitating additional measures like endpoint security or internal segmentation for comprehensive protection.
To what extent can software firewalls effectively mitigate cybersecurity threats?
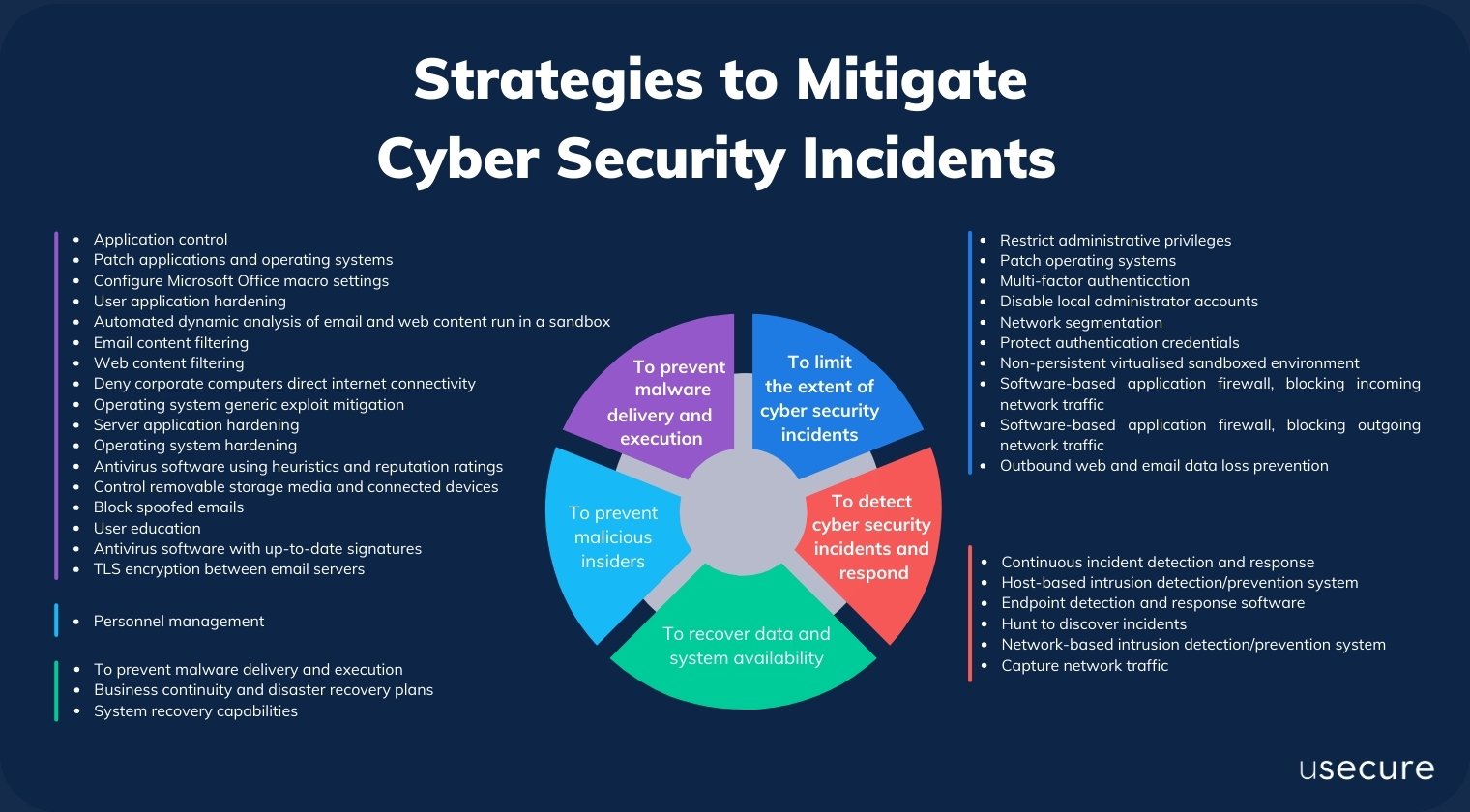
Software firewalls can effectively mitigate a significant range of cybersecurity threats by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, providing a robust barrier against unauthorized access, malware, and intrusion attempts; however, their effectiveness is inherently limited to the device they are installed on and they cannot protect against threats that bypass network-level controls, such as physical security breaches, social engineering attacks, or already embedded malware, making them a crucial but incomplete component of a layered security strategy that should be supplemented with additional measures like hardware firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and user education to comprehensively address the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Core Protective Functions of Software Firewalls
Software firewalls serve as a critical first line of defense by performing essential protective functions directly on an endpoint device. They operate by inspecting data packets and applying rule-based filtering to block unauthorized access, which helps prevent threats like network-based attacks, port scanning, and certain forms of malware from compromising the system. One of their most significant advantages is the ability to control outbound traffic, which can stop malicious software from communicating with external servers, thereby limiting data exfiltration. For many users and organizations, implementing Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection offers a straightforward and manageable security solution that is highly effective against common, unsophisticated cyber threats, though it requires regular updates and configuration to maintain efficacy against emerging risks.
Inherent Limitations and Scope of Protection
Despite their utility, software firewalls possess inherent limitations that restrict their overall effectiveness in mitigating cybersecurity threats. They are exclusively resident on individual devices and therefore offer no protection for network-wide threats, leaving other connected systems vulnerable if one device is compromised. They are largely ineffective against advanced threats such as zero-day exploits, targeted phishing attacks, or insider threats that do not rely on network traffic anomalies. Additionally, their security is contingent on the host device's integrity—if the system is already infected, the firewall's rules can potentially be disabled or bypassed by malware. The table below summarizes key limitations:
| Limitation Category | Description | Example Threats |
|---|---|---|
| Device-Specific Coverage | Protection is limited to the installed device only | Cross-system lateral movement attacks |
| Inability to Prevent All Malware | Cannot stop malware introduced via external media or user action | USB-based infections, executed phishing payloads |
| Dependence on System Health | Compromised system may render firewall ineffective | Rootkits, admin-level malware disabling protection |
Complementary Security Measures for Enhanced Defense
To maximize cybersecurity, software firewalls should be deployed as part of a multifaceted defense strategy that incorporates complementary security technologies and practices. Integrating them with hardware firewalls can provide broader network-level filtering, while antivirus and anti-malware solutions address threats that bypass network controls. Regular software updates, strong authentication mechanisms, and employee training on recognizing social engineering are vital to cover vulnerabilities that firewalls cannot address. Employing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) adds another layer by monitoring for suspicious activities and potential breaches. This holistic approach ensures that while Software Firewalls for Easy Threat Protection handle perimeter defense on endpoints, other measures collectively work to identify, isolate, and neutralize a wider spectrum of cyber risks.
More information of interest
What is a software firewall and how does it protect my computer?
A software firewall is a security program that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It acts as a barrier between your computer and potential threats from the internet or local network, blocking unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication to pass through. By filtering data packets and examining connection attempts, it provides essential protection against hackers, malware, and other cyber threats.
Do I still need a software firewall if I have a hardware firewall?
While a hardware firewall provides network-level protection for all connected devices, a software firewall adds an essential layer of individual device security. It protects against internal threats, controls outbound traffic from your specific computer, and provides customized security settings for your particular usage patterns. For comprehensive protection, experts recommend using both types of firewalls in a defense-in-depth security strategy.
How does a software firewall differ from antivirus software?
A software firewall primarily focuses on network traffic control and preventing unauthorized access to your computer, while antivirus software specializes in detecting, quarantining, and removing malicious software that has already entered your system. The firewall acts as a gatekeeper that blocks threats before they reach your computer, whereas antivirus deals with threats that have already penetrated your defenses. For complete protection, most security experts recommend using both complementary security solutions simultaneously.
Can software firewalls prevent all types of cyber threats?
While software firewalls provide crucial protection against many cyber threats, they cannot prevent all attack vectors. They are highly effective at blocking unauthorized network access and controlling traffic, but they may not protect against phishing attacks, social engineering, or already-installed malware. For comprehensive security, firewalls should be used alongside antivirus software, regular system updates, and safe computing practices to create a multi-layered defense strategy.





Deja una respuesta