
Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety
- Integrating Intrusion Detection Systems with Firewalls for Enhanced Network Protection
- Detailed Guide: Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety
- How does the integration of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) enhance the capabilities of a firewall in network security?
- To what extent does Palo Alto Networks' next-generation firewall incorporate IDS features for comprehensive threat detection?
- What constitutes an effective IDS rule configuration within a firewall's security policy framework?
- Which categories of firewalls are designed to include integrated Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) functionality?
- More information of interest
Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety, in today's interconnected digital landscape, ensuring robust network protection is paramount for organizations of all sizes. As cyber threats grow increasingly sophisticated, relying solely on traditional perimeter defenses is no longer sufficient. The integration of intrusion detection systems (IDS) with firewalls creates a more resilient security architecture capable of identifying and mitigating advanced threats in real-time.
This article explores how implementing provides comprehensive threat visibility, enhances incident response capabilities, and establishes layered defense mechanisms. By combining these technologies, enterprises can significantly strengthen their security posture against evolving cyber risks while maintaining operational continuity.
You may also be interested in reading: Top Cloud Hosting for High Availability USA
Integrating Intrusion Detection Systems with Firewalls for Enhanced Network Protection
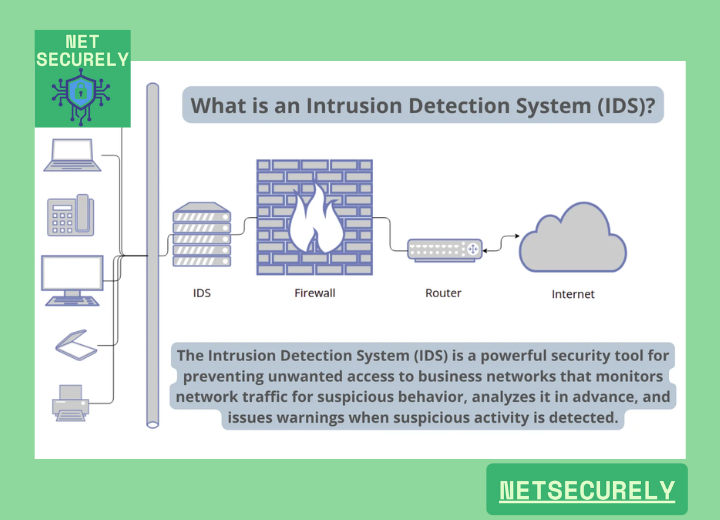
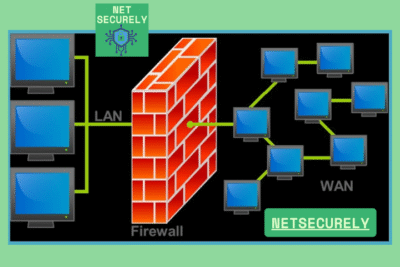
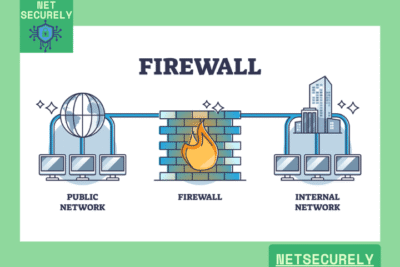
Modern network security architecture increasingly relies on the strategic combination of firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to create comprehensive defensive perimeters. While traditional firewalls act as gatekeepers by enforcing access control policies based on predetermined rules, IDS solutions provide critical monitoring capabilities that detect anomalous activities and potential security breaches. The synergy between these technologies enables organizations to implement proactive security measures rather than relying solely on reactive approaches. This integrated approach to Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety allows for real-time threat identification and automated response mechanisms, significantly reducing the window of opportunity for attackers and minimizing potential damage from security incidents.
Fundamental Components of Integrated Security Systems
Integrated security systems combining firewalls and IDS consist of several critical components working in concert. The firewall component typically includes stateful inspection capabilities, application-layer filtering, and deep packet inspection features. The IDS element incorporates signature-based detection for known threats and anomaly-based detection for identifying novel attack patterns. These systems are connected through security information and event management (SIEM) platforms that correlate data from multiple sources. The integration enables automated responses where the IDS can trigger firewall rule modifications in real-time upon detecting malicious activities, creating a dynamic defense mechanism that adapts to emerging threats.
Implementation Best Practices for Combined Solutions
Successful implementation of combined firewall and IDS solutions requires careful planning and execution. Organizations should begin with a comprehensive network assessment to identify critical assets and potential vulnerabilities. Deployment should follow a phased approach, starting with monitoring mode before enabling active blocking capabilities. Regular rulebase reviews and updates are essential to maintain effectiveness while minimizing false positives. Network segmentation should be implemented to contain potential breaches, and security policies must be documented and regularly audited. Staff training is crucial for both initial implementation and ongoing management of these integrated systems.
Threat Detection and Response Mechanisms
The combined system enhances threat detection through multiple complementary mechanisms. Signature-based detection identifies known attack patterns while behavioral analysis detects deviations from normal network activity. The integrated solution provides contextual awareness by correlating firewall log data with IDS alerts, enabling more accurate threat assessment. Upon detection, response mechanisms can range from simple alert generation to automated firewall rule modifications that block malicious traffic in real-time. This multi-layered approach significantly improves the organization's ability to detect both known and zero-day attacks while reducing response times from hours to milliseconds.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Maintaining network performance while implementing comprehensive security measures requires careful optimization. Organizations should implement traffic filtering policies that prioritize critical business applications while maintaining security standards. Hardware selection should consider throughput requirements with security features enabled, and regular performance testing should be conducted. Load balancing across multiple security devices can prevent bottlenecks, and dedicated management networks should be established to reduce overhead. Proper configuration of inspection rules and regular cleanup of unnecessary rules help maintain optimal performance without compromising security effectiveness.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Integrated firewall and IDS solutions play a crucial role in meeting various regulatory requirements and industry standards. These systems provide the auditing capabilities necessary for compliance with frameworks such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. The combination generates comprehensive logging and reporting features that demonstrate due diligence in protecting sensitive data. Regular security assessments using these integrated tools help organizations maintain continuous compliance and provide documented evidence for regulatory audits. Proper configuration ensures that security measures align with specific regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
| Security Component | Primary Function | Detection Method | Response Capability |
| Stateful Firewall | Access Control | Rule-based filtering | Packet rejection |
| Signature-based IDS | Threat Identification | Pattern matching | Alert generation |
| Anomaly-based IDS | Behavioral analysis | Statistical deviation | Traffic blocking |
| Integrated System | Comprehensive protection | Multi-layer analysis | Automated response |
Detailed Guide: Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety
How does the integration of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) enhance the capabilities of a firewall in network security?
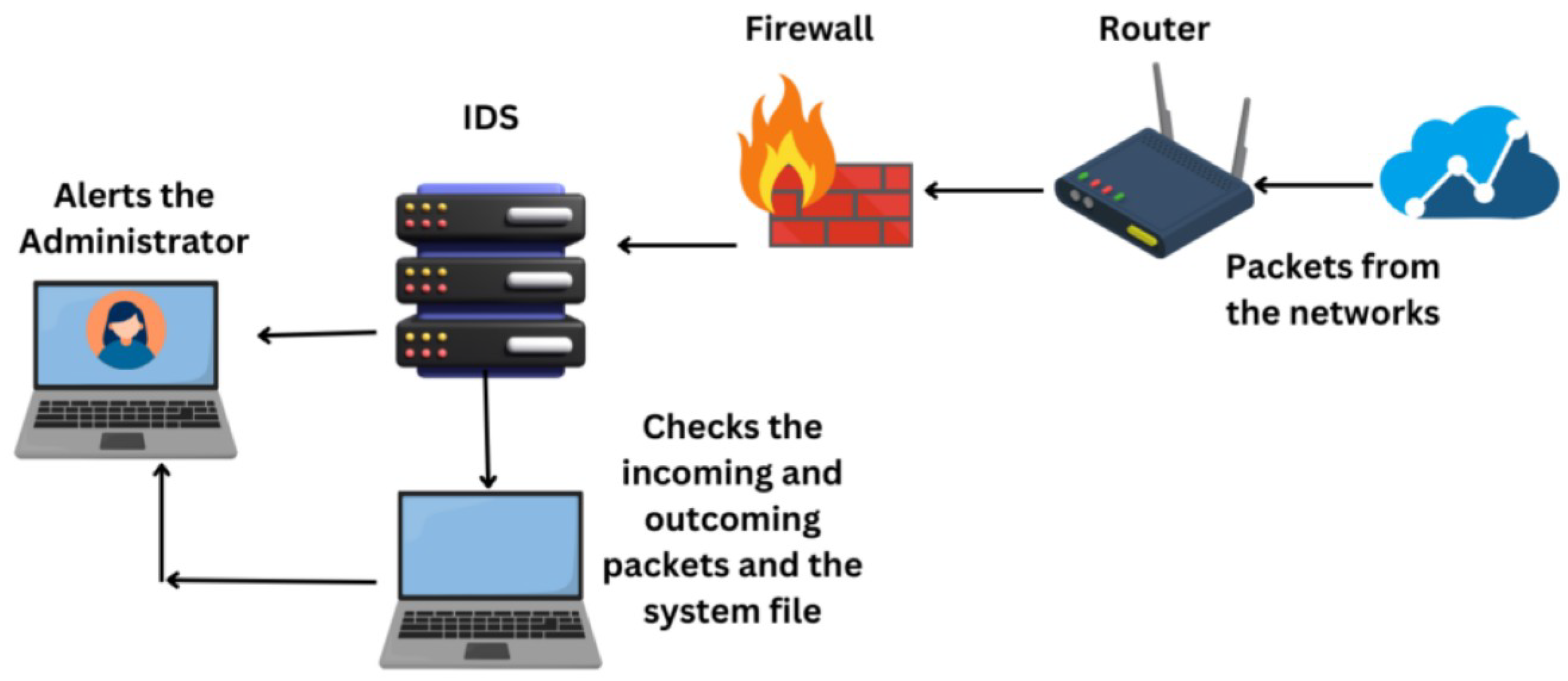
The integration of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) significantly enhances firewall capabilities by providing complementary layers of defense that address different aspects of network security. While firewalls primarily act as gatekeepers that enforce access control policies based on predefined rules, IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious patterns or anomalies that may indicate malicious activity, offering real-time analysis and alerting. This combination allows organizations to not only block unauthorized access attempts at the perimeter but also detect and respond to sophisticated threats that might bypass initial defenses, such as insider attacks or encrypted malware. By correlating firewall logs with IDS alerts, security teams gain deeper visibility into network behavior, enabling more effective incident response and threat mitigation, ultimately creating a more robust security posture through defense-in-depth strategies that help Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety.
Complementary Threat Detection Mechanisms
The integration of IDS with firewalls enhances threat detection by combining signature-based and anomaly-based methodologies. Firewalls use rule-based filtering to block known malicious IPs or ports, while IDS analyzes packet payloads and traffic patterns to identify suspicious behavior that may evade static rules. This dual approach ensures both known threats and zero-day attacks are addressed, significantly improving detection accuracy and reducing false negatives. The synergy allows for comprehensive monitoring where firewalls prevent unauthorized access and IDS provides deep packet inspection, creating a layered defense strategy that adapts to evolving threats.
| Component | Primary Function | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Firewall | Access Control | Rule-based Filtering |
| IDS | Threat Detection | Signature/Anomaly Analysis |
Enhanced Incident Response and Real-Time Alerts
Integrating IDS with firewalls improves incident response by providing real-time alerts and detailed contextual information about security events. When IDS detects anomalous activity, it can trigger immediate notifications, allowing security teams to correlate these alerts with firewall logs to understand the scope and source of an attack. This enables quicker containment and remediation, such as updating firewall rules to block malicious IPs or terminating suspicious sessions. The combined system facilitates proactive measures rather than reactive fixes, ensuring that potential breaches are addressed before they cause significant damage.
Strategic Defense-in-Depth Implementation
The combination of firewalls and IDS embodies a defense-in-depth strategy, where multiple security controls are deployed to protect network assets. Firewalls serve as the first line of defense by enforcing perimeter security, while IDS provides secondary monitoring to catch intrusions that slip through. This layered approach mitigates the risk of single points of failure and strengthens overall network resilience. By leveraging both technologies, organizations can achieve a balanced security posture that addresses both external and internal threats, ensuring comprehensive protection across all network segments.
To what extent does Palo Alto Networks' next-generation firewall incorporate IDS features for comprehensive threat detection?
Palo Alto Networks' next-generation firewalls extensively incorporate intrusion detection system (IDS) capabilities as a fundamental component of their threat prevention architecture, going beyond traditional port-based blocking to perform deep packet inspection and application-level analysis across all traffic. These firewalls utilize machine learning, behavioral analytics, and a continuously updated threat intelligence feed (WildFire) to identify known and unknown threats, including malware, exploits, and command-and-control communications. The integrated IDS/IPS functionality operates in conjunction with the firewall's App-ID, User-ID, and Content-ID technologies to provide context-aware security, enabling comprehensive threat detection that correlates network activity with application usage and user identity while maintaining Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety as a core operational principle.
Core IDS Integration in Threat Prevention Architecture
Palo Alto Networks' next-generation firewalls feature deeply integrated IDS/IPS engines that operate within the single-pass software architecture, inspecting all traffic for threats without performance degradation. This integration allows for simultaneous application identification, user mapping, and content scanning while detecting intrusions using signature-based and anomaly-based methodologies. The system employs protocol decoders for common services and applications to normalize traffic and detect evasions, with customized signatures available to address organization-specific requirements. This architectural approach ensures that IDS functionality is not a separate module but a cohesive part of the unified security policy enforcement.
Advanced Threat Detection Capabilities
The IDS features within Palo Alto Networks firewalls extend beyond traditional pattern matching to include machine learning models and behavioral analysis for identifying zero-day exploits and sophisticated attacks. These capabilities are enhanced by the WildFire cloud-based threat analysis service, which performs dynamic analysis of suspicious files and URLs, automatically generating and distributing signatures to all firewalls in the network. The system also leverages global intelligence from the Unit 42 threat research team, incorporating indicators of compromise (IOCs) and emerging threat data into the IDS rule sets. Table below summarizes key detection capabilities:
| Detection Method | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Signature-Based | Uses known patterns of attacks from continually updated database | Detection of known exploits and malware |
| Behavioral Analysis | Monitors for deviations from established baselines of normal activity | Identifying zero-day and unknown threats |
| Protocol Anomaly Detection | Identifies irregularities in network protocol implementation | Preventing evasion techniques and protocol abuse |
Operational Management and Policy Enforcement
The implementation of IDS features within Palo Alto Networks firewalls is managed through Panorama centralized management or the individual firewall's web interface, allowing for granular policy configuration and detailed logging. Security policies can be defined based on application, user, content type, and threat characteristics, with IDS/IPS rules applied as part of the same policy framework that controls access and filtering. The system provides comprehensive logging and reporting tools that correlate IDS events with other security data, enabling efficient incident investigation and response. This unified approach ensures that threat detection and prevention measures are consistently enforced across all network traffic without requiring separate infrastructure or management consoles.
What constitutes an effective IDS rule configuration within a firewall's security policy framework?
An effective IDS rule configuration within a firewall's security policy framework requires a multi-layered approach that integrates signature-based detection for known threats, anomaly-based monitoring for deviations from baseline behavior, and heuristic analysis for zero-day vulnerabilities, all while ensuring rules are regularly updated, contextually relevant to the network environment, and calibrated to minimize false positives without compromising threat visibility, thereby enabling proactive threat mitigation and alignment with organizational risk tolerance to Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety.
Core Components of IDS Rule Configuration
An effective IDS rule configuration hinges on several core components, including signature-based detection for identifying known attack patterns, anomaly-based monitoring to detect deviations from normal network behavior, and protocol analysis to scrutinize traffic for compliance with established standards. These elements must be complemented by custom rule creation tailored to specific organizational assets and threats, ensuring comprehensive coverage. Additionally, logical grouping of rules by severity and threat type, coupled with regular updates from threat intelligence feeds, maintains relevance and accuracy. The integration of these components forms a robust foundation for identifying and mitigating potential security incidents efficiently.
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Signature-Based Rules | Detect known threats | Blocking SQL injection patterns |
| Anomaly-Based Rules | Identify unusual behavior | Alert on traffic spikes |
| Protocol Analysis | Enforce protocol compliance | Flag invalid HTTP methods |
| Custom Rules | Address organization-specific risks | Monitoring access to critical servers |
Best Practices for Rule Management and Optimization
Optimal IDS rule management involves prioritizing rules based on risk assessment to focus on high-impact threats, employing threshold tuning to reduce false positives, and conducting regular reviews to retire obsolete rules while incorporating emerging threats. Automation through SIEM integration enhances correlation and response times, while testing rules in a simulated environment before deployment ensures they perform as intended without disrupting legitimate traffic. This disciplined approach maintains rule efficacy, minimizes performance overhead, and ensures the IDS operates as a responsive and efficient component within the security infrastructure.
Integration with Firewall Policies for Enhanced Security
Integrating IDS rules with firewall policies involves aligning detection mechanisms with access control lists to enable dynamic responses, such as automatically blocking malicious IP addresses or terminating suspicious sessions. This synergy allows the firewall to enforce preventive measures based on real-time IDS alerts, creating a cohesive defense strategy that extends beyond static rule sets. By correlating IDS findings with firewall configurations, organizations can implement adaptive security measures that respond to evolving threats, ensuring that network perimeters are not only guarded but also intelligently regulated to mitigate risks promptly.
Which categories of firewalls are designed to include integrated Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) functionality?
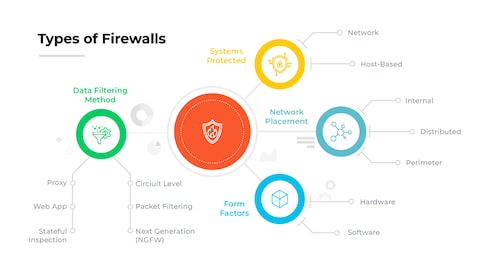
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) and unified threat management (UTM) firewalls are the categories specifically designed to include integrated Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) functionality. NGFWs combine traditional firewall capabilities with advanced features such as deep packet inspection, application awareness, and real-time threat intelligence, enabling them to actively block malicious traffic. UTMs integrate multiple security functions, including IPS, into a single appliance, providing comprehensive protection for smaller networks or businesses seeking consolidated security management. Both categories enhance network defense by proactively identifying and mitigating threats, aligning with the goal of Secure Firewalls with IDS for Network Safety.
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) with IPS
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) incorporate integrated IPS as a core component of their advanced security architecture. These firewalls go beyond port and protocol inspection by utilizing deep packet inspection (DPI) and application-level analysis to detect and block sophisticated threats in real time. NGFWs leverage threat intelligence feeds and behavioral analytics to identify anomalies, making them highly effective against zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats (APTs). The integration ensures that intrusion prevention is seamless, scalable, and context-aware, providing robust protection for modern network environments. Below is a comparison of key NGFW features with IPS:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Packet Inspection | Analyzes packet content and headers | Detects hidden malware and exploits |
| Application Awareness | Identifies and controls applications | Prevents abuse of legitimate apps |
| Threat Intelligence Integration | Uses global threat data | Blocks known malicious IPs and signatures |
| Real-Time Blocking | Immediate response to threats | Minimizes damage from attacks |
Unified Threat Management (UTM) Firewalls with IPS
Unified threat management (UTM) firewalls are designed to include integrated IPS as part of a multifunctional security suite, ideal for small to medium-sized businesses seeking all-in-one protection. UTMs consolidate features such as firewall, antivirus, anti-spam, and VPN with IPS, reducing complexity and cost while maintaining strong security posture. The IPS component in UTMs typically uses signature-based detection and heuristic analysis to monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns, though it may lack the depth of specialized NGFW systems. This integrated approach ensures that organizations can deploy comprehensive security without managing multiple discrete devices.
Comparison of NGFW and UTM IPS Capabilities
While both NGFWs and UTMs include integrated IPS, their capabilities and target use cases differ significantly. NGFWs are built for high-performance environments, offering granular control, advanced threat detection, and scalability for large enterprises, with IPS deeply embedded into their application-aware architecture. UTMs provide a cost-effective, consolidated solution for smaller networks, with IPS as one of many features, often prioritizing ease of use over advanced customization. The choice between them depends on factors such as network size, budget, and the need for specialized security functions, with NGFWs excelling in threat prevention for complex infrastructures and UTMs serving well for streamlined operations.
More information of interest
What is the difference between a firewall and an intrusion detection system (IDS)?
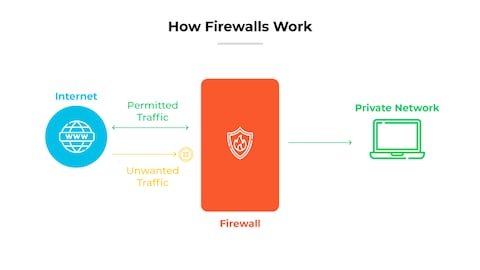
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, acting as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks. An intrusion detection system (IDS), on the other hand, is a monitoring system that detects suspicious activities and alerts administrators, but does not take direct action to block threats. Combining both provides a layered defense, with the firewall enforcing access policies and the IDS identifying potential breaches.
How does integrating an IDS with a firewall enhance network security?
Integrating an IDS with a firewall enhances network security by providing both preventive and detective capabilities. The firewall blocks unauthorized access and filters traffic in real-time, while the IDS analyzes traffic for signs of malicious activity, such as attacks or policy violations. This combination allows for immediate threat mitigation and detailed forensic analysis, improving overall resilience against sophisticated cyber threats.
What types of threats can a firewall with IDS protect against?
A firewall with IDS can protect against a wide range of threats, including unauthorized access, malware, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and network intrusions. The firewall prevents unauthorized traffic from entering the network, while the IDS detects anomalies such as suspicious patterns, known attack signatures, or behaviors that deviate from normal network activity, providing comprehensive coverage against both external and internal threats.
What are the best practices for configuring a firewall with IDS?
Best practices for configuring a firewall with IDS include regularly updating rule sets and signatures, segmenting the network to limit the spread of threats, monitoring logs continuously for alerts, and testing the system periodically to ensure optimal performance. It is also crucial to tailor rules to your specific network environment and maintain a balance between security and network performance to avoid unnecessary disruptions.



Deja una respuesta