Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection
- Integrating Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection
- Comprehensive Guide to Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection
- How can firewalls incorporate intrusion detection systems (IDS) for enhanced security monitoring?
- Does the Palo Alto Networks firewall platform include integrated intrusion detection capabilities?
- What distinguishes a web application firewall (WAF) from an intrusion prevention system (IPS) with IDS functionality?
- Which firewall types natively integrate intrusion prevention system (IPS) features?
- More information of interest
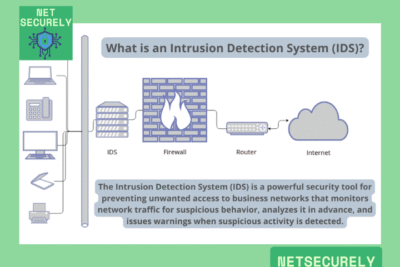
, Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection, in today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape, organizations require robust cybersecurity measures to defend against sophisticated attacks. Traditional firewalls, while essential, are no longer sufficient on their own to counter dynamic threats. The integration of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) with firewalls has emerged as a critical advancement, offering comprehensive network security. provide continuous monitoring, immediate threat identification, and automated responses to potential breaches.
This synergy enhances defense mechanisms by combining proactive filtering with intelligent analysis, ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed instantly, minimizing risks, and safeguarding sensitive data in an increasingly interconnected digital environment.
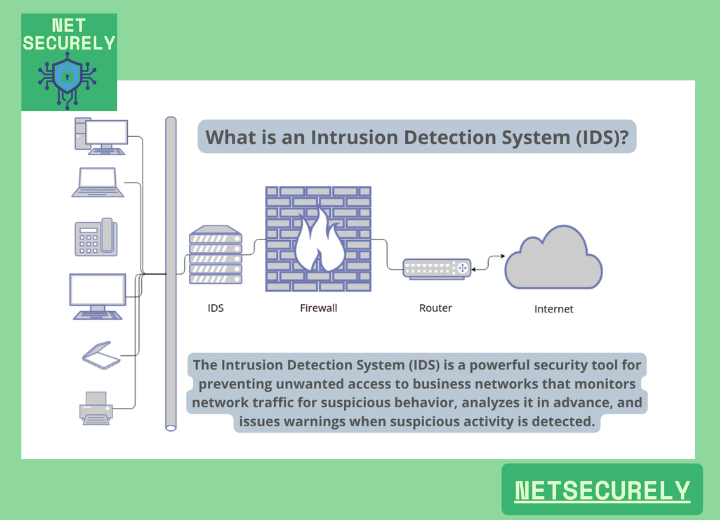
Integrating Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection
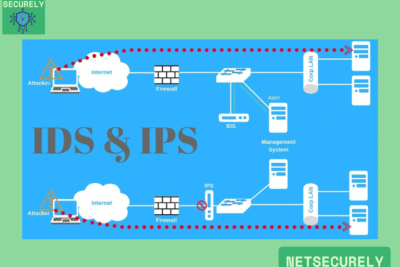
Integrating firewalls with Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) creates a robust cybersecurity framework designed for real-time protection. This combination enhances network security by actively monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats as they occur. Firewalls act as a barrier, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules, while IDS analyzes traffic for suspicious patterns or anomalies. When integrated, they provide a layered defense mechanism, ensuring immediate threat identification and mitigation, which is critical for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining operational integrity.
How Firewalls and IDS Work Together for Real-Time Protection
Firewalls and IDS complement each other by operating at different layers of network security. The firewall enforces access policies and blocks unauthorized traffic, while the IDS monitors network packets for signs of malicious activity. In a real-time protection setup, the IDS alerts the firewall to immediately block suspicious IP addresses or terminate connections, preventing potential breaches before they cause harm.
Key Benefits of Using Firewalls with IDS
The integration offers several advantages, including enhanced threat detection, reduced false positives, and automated responses. By correlating firewall logs with IDS alerts, organizations gain a comprehensive view of network activity, enabling quicker decision-making and more effective security management.
Types of Threats Detected by This Combined System
This system identifies a wide range of threats, such as DDoS attacks, malware intrusions, port scans, and unauthorized access attempts. The real-time analysis ensures that both known and emerging threats are caught early, minimizing their impact.
Implementation Best Practices for Maximum Efficiency
To maximize efficiency, ensure proper configuration of both components, regular updates of threat signatures, and continuous monitoring. It is also advisable to integrate with a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system for centralized log analysis and response coordination.
Challenges and Considerations in Deployment
Deploying Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection can present challenges, including performance overhead, complexity in configuration, and the need for skilled personnel. Organizations must balance security needs with network performance and ensure adequate training for staff.
| Component | Primary Function | Role in Real-Time Protection |
| Firewall | Traffic Filtering | Blocks unauthorized access based on rules |
| IDS | Threat Detection | Monitors and alerts on suspicious activity |
| Integrated System | Unified Defense | Combines filtering and detection for immediate response |
Comprehensive Guide to Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection
How can firewalls incorporate intrusion detection systems (IDS) for enhanced security monitoring?
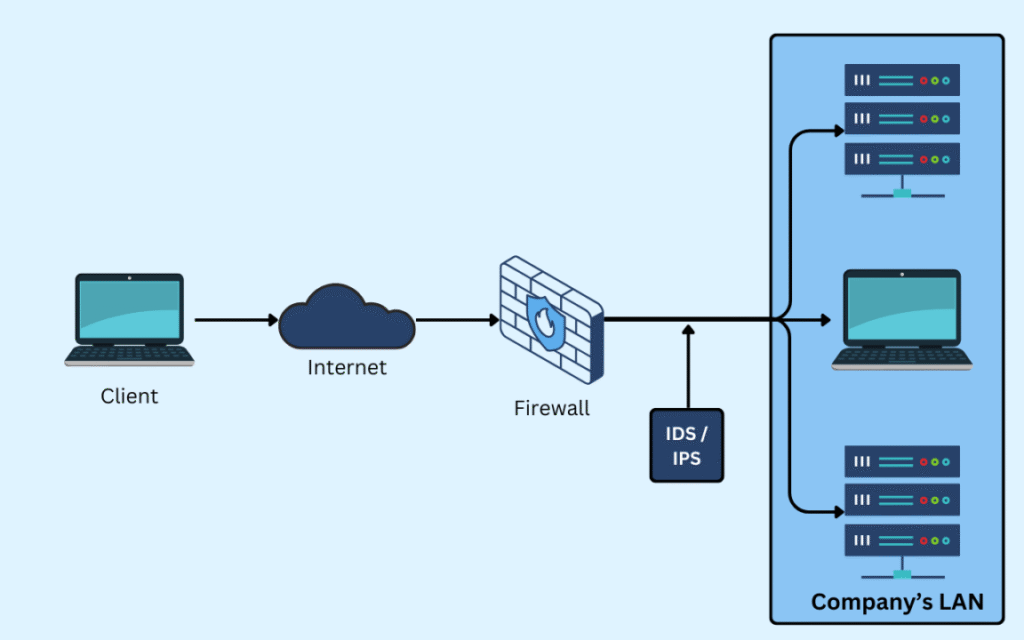
Firewalls can incorporate intrusion detection systems (IDS) through integrated deployment models, where the firewall either includes a built-in IDS module or operates in tandem with a standalone IDS via network traffic mirroring or API-based communication. This integration enables the firewall to perform deep packet inspection beyond traditional rule-based filtering, analyzing traffic for anomalous patterns, known attack signatures, or behavioral deviations that may indicate malicious activity. By correlating firewall logs with IDS alerts, security teams gain enhanced visibility into potential threats, allowing for immediate blocking of suspicious IP addresses or sessions, thereby creating a more proactive defense mechanism. Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection can thus not only prevent unauthorized access but also detect and respond to sophisticated attacks like zero-day exploits or lateral movement within the network.
Integrated Deployment Models
Integrated deployment models involve embedding IDS functionality directly into the firewall infrastructure, either as a unified threat management (UTM) feature or through hardware/software modules that enable simultaneous packet filtering and intrusion analysis. This approach reduces latency by processing traffic within a single device, allowing for immediate action on detected threats without relying on external systems. The firewall's rule set can be dynamically updated based on IDS findings, enhancing responsiveness to emerging risks. For example, if the IDS identifies a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack pattern, the firewall can automatically enforce rate-limiting rules or block malicious IP ranges.
Traffic Analysis and Signature Detection
Firewalls with integrated IDS leverage deep packet inspection (DPI) and signature-based detection to identify known threats by comparing network traffic against a database of malicious patterns, such as SQL injection strings or malware signatures. This process involves examining both header and payload data to detect anomalies that evade conventional firewall rules. The system can be configured with custom signatures for organization-specific threats, improving accuracy. Additionally, protocol analysis ensures compliance with standard communication norms, flagging deviations that may indicate exploitation attempts. The table below summarizes key detection techniques:
| Technique | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Signature-Based | Matches traffic to known attack patterns | Blocking packets containing DROP TABLE commands |
| Anomaly-Based | Detects deviations from baseline behavior | Flagging unusual port scanning activity |
| Protocol Analysis | Validates adherence to protocol standards | Identifying malformed HTTP requests |
Response Mechanisms and Alert Integration
Upon detecting a threat, integrated firewall-IDS systems execute automated response actions, such as blocking source IP addresses, terminating sessions, or quarantining affected devices to mitigate damage. These responses are guided by predefined policies that balance security and operational continuity. Alerts are generated in real-time and forwarded to a security information and event management (SIEM) system for correlation with other logs, enabling comprehensive incident analysis. The firewall can also trigger custom scripts or API calls to third-party tools for expanded remediation, such as isolating compromised endpoints via endpoint detection and response (EDR) platforms.
Does the Palo Alto Networks firewall platform include integrated intrusion detection capabilities?
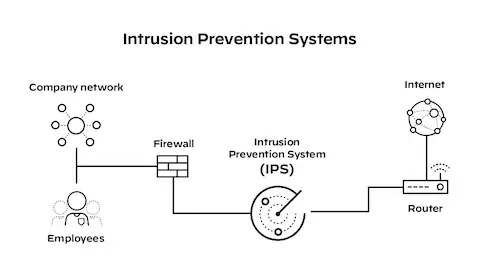
Yes, the Palo Alto Networks firewall platform includes integrated intrusion detection capabilities as a core component of its security functionality, utilizing advanced threat prevention technologies that combine signature-based detection, behavioral analytics, and machine learning to identify and block malicious activities across networks, applications, and users in real-time, ensuring comprehensive protection against known and unknown threats while maintaining granular visibility and control over traffic flows through its next-generation firewall architecture.
Intrusion Detection System Integration
The Palo Alto Networks platform integrates a sophisticated Intrusion Detection System (IDS) that works in tandem with its firewall capabilities to monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns and known attack signatures, leveraging global threat intelligence and custom rules to provide real-time alerts and automated responses, thereby enhancing the overall security posture without requiring separate hardware or software deployments.
Advanced Threat Prevention Features
Beyond traditional IDS, the platform incorporates Advanced Threat Prevention features, including inline deep packet inspection, SSL decryption, and cloud-delivered security services, which enable it to detect and mitigate zero-day exploits, malware, and command-and-control communications effectively, ensuring that Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection operate at the highest level of efficacy against evolving cyber threats.
Comparison with Traditional Firewalls
Unlike traditional firewalls that primarily focus on port and protocol filtering, Palo Alto Networks' solution combines stateful inspection with integrated IDS/IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), application-level controls, and user identity tracking, creating a multi-layered defense mechanism; the table below highlights key differences:
| Feature | Traditional Firewall | Palo Alto Networks Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Intrusion Detection | Often add-on or separate system | Fully integrated with real-time analysis |
| Threat Prevention | Limited to signatures | Behavioral and ML-based detection |
| Application Awareness | Minimal or none | Granular application control and visibility |
What distinguishes a web application firewall (WAF) from an intrusion prevention system (IPS) with IDS functionality?
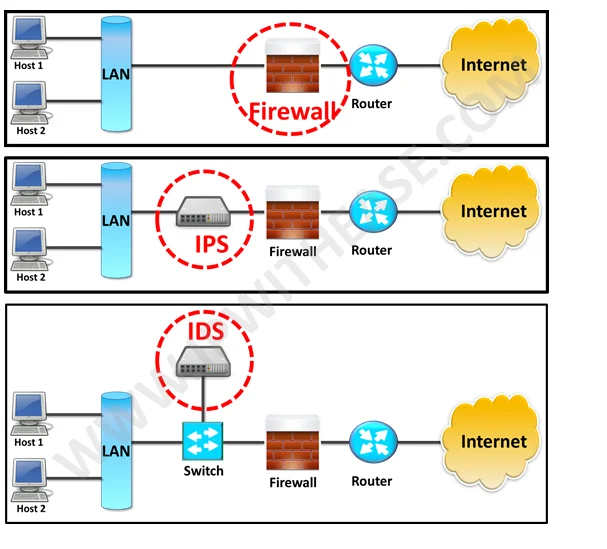
A web application firewall (WAF) distinguishes itself from an intrusion prevention system (IPS) with IDS functionality primarily through its specialized focus on application-layer traffic, where it inspects and filters HTTP/HTTPS requests to protect against web-specific threats like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, whereas an IPS operates at the network and transport layers, monitoring broader network traffic for a wide range of malicious activities such as exploits, malware, and policy violations, with IDS functionality providing detection without blocking; while both can offer real-time protection, a WAF is context-aware of web applications, making it more effective against sophisticated application attacks, whereas an IPS is designed for comprehensive network security, and some advanced solutions integrate both, such as Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection, to provide layered defense.
Layer of Operation and Protocol Focus
The primary distinction lies in the operational layer and protocol specificity: a WAF operates exclusively at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model, deeply inspecting HTTP/HTTPS traffic to defend against web-based exploits like injection attacks or session hijacking, while an IPS functions at the network (Layer 3) and transport (Layer 4) layers, analyzing IP packets, TCP/UDP streams, and broader network protocols to detect and prevent intrusions such as port scans, DDoS attacks, or known vulnerabilities across services, with its IDS component providing alerting capabilities; this makes a WAF indispensable for securing web applications, whereas an IPS safeguards the entire network infrastructure.
Threat Detection and Mitigation Capabilities
WAFs and IPSs differ significantly in their threat detection methodologies and mitigation approaches: a WAF employs techniques like signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and positive/negative security models to identify and block web-specific attacks, often leveraging custom rules for applications, while an IPS uses signature matching, anomaly detection, and protocol analysis to halt network-level threats, including exploits targeting services like FTP or SSH, and its IDS functionality allows monitoring without intervention; for example, a WAF might stop a malicious API request, whereas an IPS could quarantine a host spreading malware, and integrated systems like Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection enhance coverage by combining these strengths.
| Feature | Web Application Firewall (WAF) | Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Layer | Application Layer (L7) | Network/Transport Layers (L3-L4) |
| Key Protocols | HTTP/HTTPS, WebSockets | IP, TCP, UDP, ICMP |
| Common Threats Blocked | SQLi, XSS, CSRF | Exploits, DDoS, Malware |
| Deployment Point | Near Web Servers/Applications | Network Perimeter/Internal Segments |
| IDS Functionality | Rarely included | Core component for detection |
Deployment and Integration Scenarios
Deployment strategies highlight further differences: a WAF is typically deployed close to web applications, either as a cloud-based service, on-premises appliance, or software module, to minimize latency and tailor protection to specific apps, while an IPS is placed at network chokepoints like gateways or between segments to monitor all traffic, and its IDS mode can be used for passive analysis; integration varies, with WAFs often part of a application security suite and IPSs embedded in next-generation firewalls or standalone devices, and modern solutions may combine both, such as Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection, to address multi-layer threats efficiently.
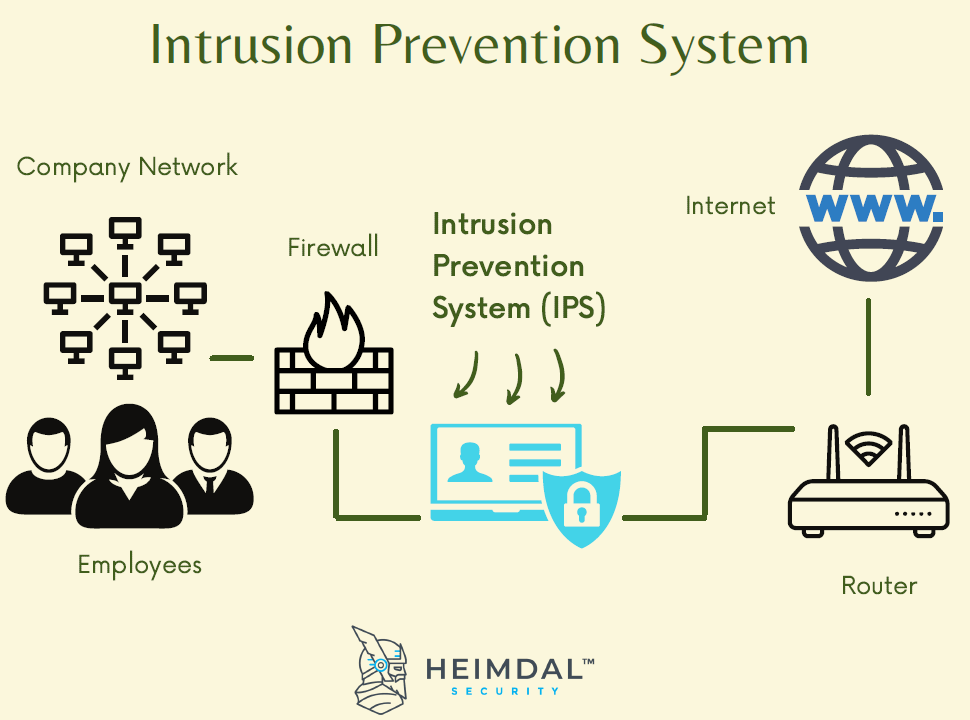
Which firewall types natively integrate intrusion prevention system (IPS) features?
_.png)
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) natively integrate intrusion prevention system (IPS) features by combining deep packet inspection, application awareness, and threat intelligence to actively block malicious traffic in real-time, while unified threat management (UTM) firewalls incorporate IPS as part of their all-in-one security suite, and cloud firewalls (such as those in cloud-native platforms) often include built-in IPS capabilities to protect virtualized and cloud-based environments, with some enterprise-grade hardware firewalls also offering integrated IPS modules for enhanced network security.
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs)
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) inherently include intrusion prevention system (IPS) functionality as a core component, leveraging advanced techniques like deep packet inspection, application-level analysis, and real-time threat intelligence feeds to detect and block attacks proactively. These firewalls go beyond traditional port and protocol filtering by examining the actual content of network traffic, enabling them to identify and mitigate threats such as malware, exploits, and unauthorized access attempts. Firewalls with IDS for Real-Time Protection often refer to NGFWs that seamlessly blend intrusion detection and prevention, providing a unified defense mechanism. The table below summarizes key IPS features typically integrated into NGFWs:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Deep Packet Inspection | Analyzes packet payloads for malicious content |
| Application Awareness | Identifies and controls applications regardless of port |
| Threat Intelligence Integration | Uses updated databases to recognize known threats |
| Real-Time Blocking | Actively drops or alters malicious traffic in real-time |
Unified Threat Management (UTM) Firewalls
Unified threat management (UTM) firewalls natively integrate intrusion prevention system (IPS) features as part of their consolidated security approach, which typically includes firewall, antivirus, content filtering, and VPN capabilities in a single device or software solution. These systems are designed for ease of use and are often deployed in small to medium-sized businesses where comprehensive, all-in-one security is prioritized. The IPS component in UTMs monitors network traffic for suspicious patterns and known attack signatures, automatically taking action to prevent breaches. Key aspects of UTM firewalls with integrated IPS are outlined in the table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Signature-Based Detection | Matches traffic against a database of known threats |
| Centralized Management | Provides a single interface for all security functions |
| Automated Responses | Blocks or alerts on detected intrusions without manual intervention |
| Scalability | Suited for environments needing multiple integrated security layers |
Cloud and Virtual Firewalls
Cloud and virtual firewalls frequently incorporate native intrusion prevention system (IPS) features to secure dynamic and scalable cloud infrastructures, utilizing agent-based or gateway-level inspection to monitor traffic between virtual machines, containers, and cloud services. These firewalls are essential in environments where traditional hardware perimeters are absent, and they rely on software-defined policies to enforce security. The integrated IPS capabilities help detect and prevent attacks targeting cloud-specific vulnerabilities, such as misconfigurations or API exploits. The table highlights common attributes:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Software-Defined Security | Applies policies dynamically across cloud resources |
| API Integration | Monitors and protects cloud service interactions |
| Elastic Scalability | Adapts IPS processing to variable cloud workloads |
| Micro-Segmentation Support | Enforces fine-grained security zones within the cloud |
More information of interest
What is the primary advantage of combining a firewall with an intrusion detection system (IDS)?
The key advantage of integrating a firewall with an intrusion detection system (IDS) is the ability to provide real-time protection by not only blocking unauthorized access but also actively monitoring and analyzing network traffic for suspicious activities, enabling immediate threat detection and response.
How does an IDS enhance the functionality of a traditional firewall?
An IDS enhances a traditional firewall by adding deep packet inspection and behavioral analysis capabilities, allowing it to identify and alert on potential threats like malware, exploits, or policy violations that might bypass standard firewall rules.
Can a firewall with IDS prevent zero-day attacks?
While no system can guarantee complete prevention of zero-day attacks, a firewall with integrated IDS improves defenses by using anomaly-based detection and heuristic analysis to identify unusual behavior patterns, potentially flagging and mitigating previously unknown threats in real time.
What are the common deployment modes for firewalls with IDS capabilities?
Common deployment modes include inline deployment, where the system actively blocks threats in real time, and passive monitoring, where it analyzes traffic copies to detect and alert on intrusions without interrupting network flow, balancing security and performance needs.



Deja una respuesta