
Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting

- Essential Security Features for Your Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting
- Best Practices for a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting
- What are the key considerations for hosting websites on a secure Linux VPS?
- What security measures should be implemented to protect a Linux VPS for web applications?
- How does a secure Linux VPS compare to traditional shared web hosting for performance and security?
- Which Linux distributions are most suitable for running a secure VPS environment?
- More information of interest
Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting, in today's digital landscape, the demand for robust and reliable hosting solutions continues to grow exponentially. A offers an optimal balance of performance, control, and security for modern web applications. By leveraging the inherent stability of Linux and advanced isolation technologies, this hosting environment provides a fortified foundation against threats while ensuring scalable resources.
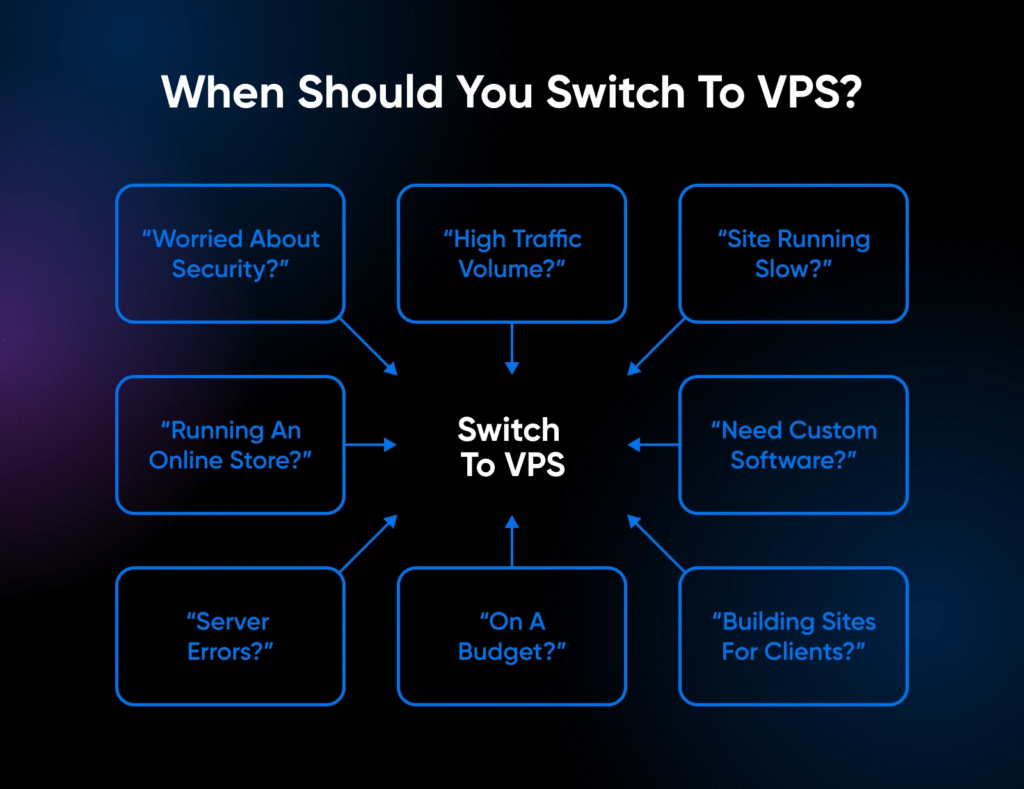
Whether deploying enterprise applications or high-traffic websites, implementing a ensures enhanced data protection, customizable configurations, and superior uptime—making it an indispensable choice for developers and businesses prioritizing security and efficiency.
Essential Security Features for Your Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting
A Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting forms the backbone of reliable and protected online services, combining robust operating system architecture with tailored security configurations. This environment ensures that web applications and hosting services operate with minimized vulnerabilities, guarding against unauthorized access, data breaches, and service disruptions. Implementing a hardened Linux VPS involves multiple layers of security, from the initial setup and system hardening to ongoing maintenance and monitoring, all designed to maintain integrity, confidentiality, and availability of hosted resources.
Initial Setup and Hardening Steps
The foundation of a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting begins with a meticulously configured initial setup. This includes installing the latest stable distribution, applying all security patches during deployment, and disabling unnecessary services to reduce the attack surface. Key steps involve setting up a non-root user with sudo privileges, configuring a firewall (such as UFW or firewalld), and ensuring SSH access is secured with key-based authentication and disabled root login. These measures establish a baseline of protection before any applications are deployed.
Network Security and Firewall Configuration
Network security is critical for safeguarding a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting. Configuring a firewall to allow only essential ports (e.g., 80, 443, and a custom SSH port) blocks unauthorized traffic. Additionally, tools like Fail2Ban can be implemented to prevent brute-force attacks by monitoring and banning suspicious IP addresses. Employing VPNs or private networks for administrative access further enhances security, ensuring that sensitive management interfaces are not exposed to the public internet.
Application and Service Hardening
Hardening applications and services on a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting involves configuring software to run with least privilege and applying security-specific settings. For web servers like Apache or Nginx, this includes disabling server tokens, using secure protocols (TLS 1.2+), and implementing security headers. Database services (e.g., MySQL or PostgreSQL) should be configured with strong passwords, restricted remote access, and encrypted connections. Regular updates and monitoring for vulnerabilities are essential to maintain a secure posture.
Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
Proactive monitoring and intrusion detection are vital for maintaining a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting. Tools like AIDE (Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment) or Tripwire can monitor file integrity, alerting administrators to unauthorized changes. Log management solutions (e.g., Logwatch or centralized logging) help track system and application activities, while intrusion detection systems (IDS) such as Suricata provide real-time network monitoring. Setting up alerts for suspicious activities enables rapid response to potential threats.
Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
A comprehensive backup and disaster recovery strategy is indispensable for a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting. Regular, encrypted backups of both system configurations and application data ensure quick recovery in case of data loss, corruption, or security incidents. Automating backups to off-site or cloud storage and periodically testing restoration procedures guarantee that services can be resumed with minimal downtime. This approach mitigates risks and supports business continuity.
| Security Feature | Description | Implementation Tool/Example |
| Firewall | Controls inbound and outbound network traffic | UFW, firewalld |
| SSH Hardening | Secures remote server access | Key-based auth, custom port |
| Intrusion Detection | Monitors for unauthorized activities | Fail2Ban, AIDE |
| Backups | Ensures data recovery capability | Automated scripts, off-site storage |
| Service Hardening | Minimizes application vulnerabilities | Disable unused modules, TLS config |
Best Practices for a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting
What are the key considerations for hosting websites on a secure Linux VPS?

When hosting websites on a secure Linux VPS, key considerations include selecting a reputable hosting provider with robust infrastructure, implementing strong SSH key authentication and disabling password logins, configuring a firewall (like UFW or firewalld) to restrict unnecessary ports, regularly updating the system and software packages to patch vulnerabilities, installing and configuring security tools such as Fail2Ban to prevent brute-force attacks, setting up automated backups with off-site storage, using SSL/TLS certificates for encrypted connections, and employing monitoring solutions to detect anomalies; these measures collectively ensure a resilient environment for running web applications, making it an ideal Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting.
Server Hardening and Configuration
Server hardening involves securing the base operating system by removing unused packages, disabling unnecessary services, and configuring strict permissions; key steps include setting up SELinux or AppArmor for access control, enabling automatic security updates, and using tools like Lynis for auditing. A well-hardened server reduces the attack surface and ensures compliance with security best practices, which is critical for maintaining a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting. Below is a table summarizing essential hardening actions:
| Action | Purpose | Tool/Command Example |
|---|---|---|
| Disable root SSH login | Prevents direct root access attacks | Edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config: PermitRootLogin no |
| Configure firewall rules | Restricts network access to necessary ports | ufw allow 80,443; ufw enable |
| Install and configure Fail2Ban | Blocks brute-force attempts | apt install fail2ban; systemctl enable fail2ban |
| Set strict file permissions | Limits unauthorized file modifications | chmod 750 /var/www/html; chown www-data:www-data |
Network Security and Monitoring
Network security focuses on protecting the VPS from external threats by implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and encrypted communications; essential practices include using VPNs for administrative access, monitoring network traffic with tools like Wireshark or tcpdump, and configuring DDoS protection if offered by the provider. Continuous monitoring with solutions such as Nagios or Prometheus helps detect suspicious activities early, ensuring the integrity and availability of services hosted on the VPS.
Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
A comprehensive backup strategy is vital to mitigate data loss from incidents like hardware failures, cyberattacks, or human errors; this includes scheduling automated daily or weekly backups of both website files and databases, storing copies in off-site or cloud locations (e.g., AWS S3 or Backblaze), and regularly testing restoration procedures to verify reliability. Implementing version control for code and using incremental backups can optimize storage and recovery time, safeguarding business continuity for web applications hosted on the VPS.
What security measures should be implemented to protect a Linux VPS for web applications?

To Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting, implement strong SSH security by disabling root login and using key-based authentication, configure a firewall like UFW or firewalld to restrict unnecessary ports, keep the system and software updated with security patches, install and configure fail2ban to prevent brute-force attacks, utilize SELinux or AppArmor for access control, regularly audit user accounts and permissions, encrypt sensitive data and communications with SSL/TLS, set up isolated environments for applications using containers or virtualization, and maintain frequent backups with tested recovery procedures.
SSH and Access Control
To secure remote access, always disable password-based authentication and root login for SSH, enforce the use of SSH key pairs with passphrase protection, change the default SSH port from 22 to a non-standard one, and employ tools like fail2ban to automatically block IP addresses after multiple failed login attempts. Implement strict user privilege management through sudo access controls and regularly review user accounts to remove or disable inactive ones, ensuring only authorized personnel have access to the system.
Firewall and Network Security
Configure a robust firewall such as UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) or firewalld to allow only essential inbound and outbound traffic, typically limiting access to ports 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), and your custom SSH port while denying all others. Utilize iptables for more granular rule sets if needed, and consider implementing DDoS protection measures or network-level security through your hosting provider. Regularly monitor network activity with tools like tcpdump or Wireshark to detect and respond to suspicious behavior promptly.
Application and Service Hardening
Harden all running services and web applications by keeping them updated with the latest security patches, disabling unused services to reduce the attack surface, and using SELinux or AppArmor to enforce mandatory access controls. For web apps, employ a Web Application Firewall (WAF) like ModSecurity, configure proper file permissions and ownership, store sensitive data such as database credentials in environment variables or encrypted files, and regularly scan for vulnerabilities using tools like Lynis or OpenVAS.
| Security Measure | Tool/Implementation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| SSH Hardening | Disable root login, use key-based auth | Prevent unauthorized access |
| Firewall Configuration | UFW, firewalld, iptables | Control network traffic |
| Intrusion Prevention | fail2ban, SELinux, AppArmor | Block attacks and enforce policies |
| Web App Protection | ModSecurity, SSL/TLS, updates | Secure application layer |
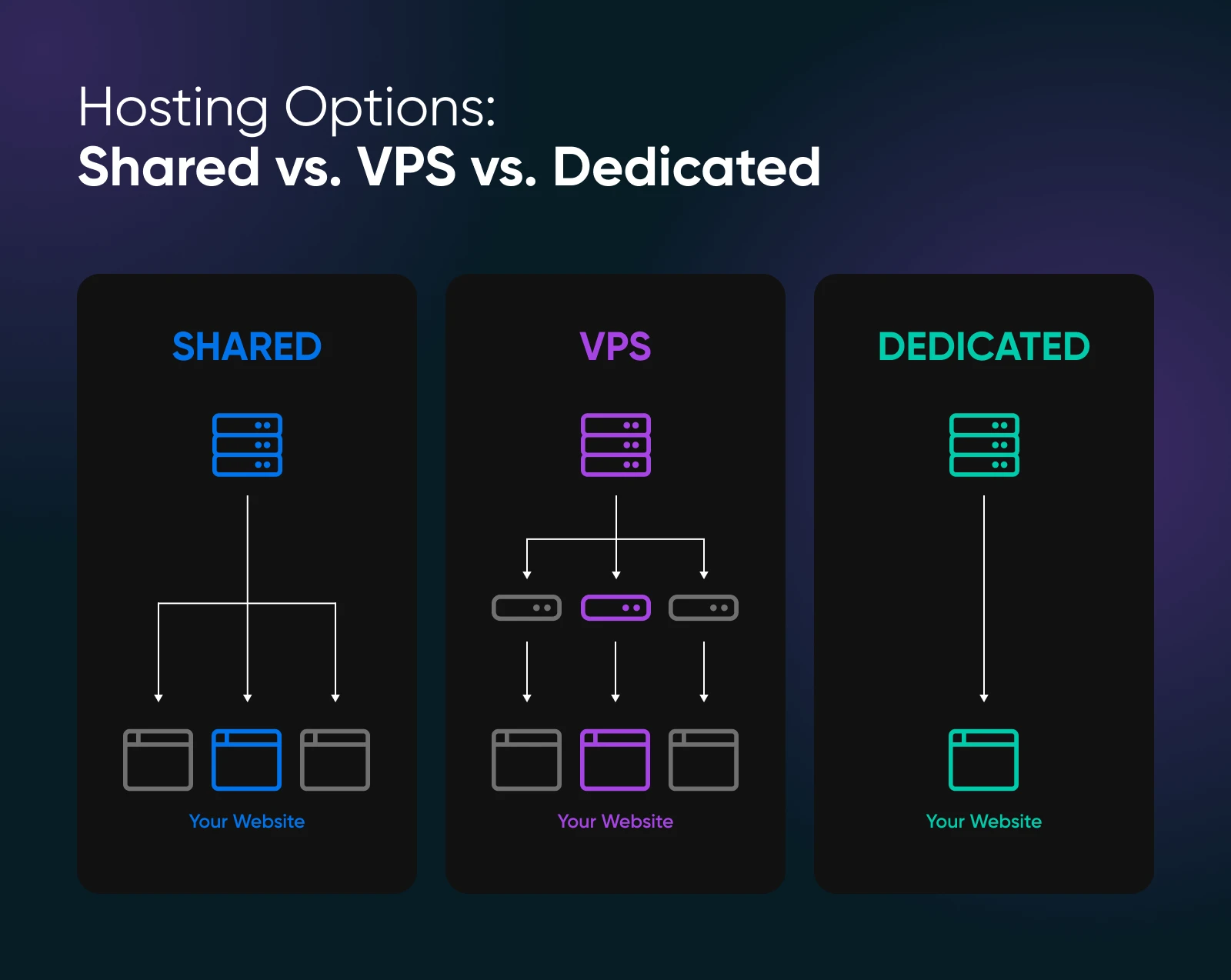
A secure Linux VPS offers superior performance and security compared to traditional shared hosting by providing dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage, ensuring consistent performance even under high traffic, and isolating your environment from other users to eliminate cross-contamination risks, whereas shared hosting pools resources among multiple clients, leading to potential slowdowns and vulnerabilities from neighboring accounts; additionally, with a VPS, you have full root access to implement custom security configurations, firewalls, and regular updates, making it ideal for a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting where control and reliability are critical, while shared hosting relies on the provider's generic security measures, which may not be as stringent or tailored to specific needs.
Performance Comparison: Resource Allocation and Scalability
In terms of performance, a secure Linux VPS provides dedicated resources including CPU, RAM, and disk I/O, which ensures that your applications run smoothly without being affected by other users on the same server, whereas traditional shared hosting involves resource sharing among multiple clients, often resulting in unpredictable performance drops during peak usage times; moreover, VPS hosting allows for easy scalability, enabling you to upgrade resources as your needs grow, while shared hosting plans typically have fixed limits that can constrain expansion and responsiveness for demanding web applications.
Security Advantages: Isolation and Customization
From a security perspective, a secure Linux VPS offers enhanced isolation through virtualization, which means that your server environment is completely separate from others, drastically reducing the risk of malware propagation or unauthorized access from neighboring accounts, and it grants full root access for implementing tailored security measures such as custom firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and automated patches; in contrast, shared hosting operates on a single server with multiple users, relying on the provider's generalized security protocols that may not address specific vulnerabilities or allow for advanced configurations, making it less secure for sensitive data or high-stakes applications.
Cost and Management Considerations
When evaluating cost and management, a secure Linux VPS typically involves a higher initial investment and requires more technical expertise for setup, maintenance, and security oversight, as you are responsible for managing the server environment, whereas shared hosting is more cost-effective and user-friendly, with the provider handling most administrative tasks, though this convenience comes at the expense of limited control and potential performance bottlenecks; the table below summarizes key differences to help in decision-making based on priorities like budget, control, and requirements for Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting.
| Aspect | Secure Linux VPS | Shared Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Type | Dedicated (Guaranteed) | Shared (Variable) |
| Security Control | Full Root Access | Provider-Managed |
| Performance Impact | Consistent and Isolated | Subject to Neighbor Usage |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher Cost, More Control | Lower Cost, Less Control |
| Technical Skill Needed | Advanced | Basic |
Which Linux distributions are most suitable for running a secure VPS environment?

For running a secure VPS environment, Debian, AlmaLinux, and OpenSUSE are among the most suitable Linux distributions due to their strong security features, long-term support, and stability. Debian is renowned for its rigorous testing process and extensive security updates, making it ideal for servers requiring high reliability. AlmaLinux, as a RHEL-compatible distribution, offers robust security tools like SELinux and timely patches, ensuring enterprise-grade protection. OpenSUSE provides advanced security configurations through YaST and supports AppArmor, making it versatile for both novice and experienced administrators. These distributions also benefit from active communities and extensive documentation, which are crucial for maintaining a Secure Linux VPS for Web Apps and Hosting.
Debian for Stability and Security
Debian is highly regarded for its unwavering commitment to stability and security, making it an excellent choice for VPS environments. The distribution undergoes extensive testing before releases, ensuring that software is vetted for vulnerabilities, and it provides long-term support with regular security updates. Its minimal installation footprint reduces the attack surface, while integrated tools like AppArmor and Debian Security Advisories help maintain a hardened server. For administrators seeking a reliable, community-driven OS with a proven track record in secure deployments, Debian stands out as a top contender.
AlmaLinux as a RHEL Alternative
AlmaLinux serves as a robust, free alternative to Red Hat Enterprise Linux, offering similar security features and compatibility. It includes SELinux for mandatory access control, along with timely security patches and updates aligned with RHEL's lifecycle. AlmaLinux is particularly suited for enterprises and developers requiring a stable, predictable environment with strong security defaults. The distribution also supports CIS benchmarks and hardening scripts, facilitating compliance and enhanced protection for critical workloads.
OpenSUSE with Advanced Security Tools
OpenSUSE provides a flexible and secure foundation for VPS deployments, featuring comprehensive tools like YaST for system configuration and AppArmor for application-level security. The distribution offers both a stable release (Leap) and a rolling version (Tumbleweed), catering to different security and update preferences. With built-in support for Btrfs snapshots and automated testing, OpenSUSE enhances reliability and recovery options, making it suitable for environments where security and adaptability are priorities.
| Distribution | Key Security Feature | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Debian | AppArmor, Long-Term Support | Stable, General-Purpose Servers |
| AlmaLinux | SELinux, RHEL Compatibility | Enterprise Applications |
| OpenSUSE | YaST, Btrfs Snapshots | Flexible and Configurable setups |
More information of interest
What security features are included with a Secure Linux VPS for web applications?
Our Secure Linux VPS includes firewall configurations, DDoS protection, regular security updates, and SSH key authentication to ensure your web applications are protected against common threats and vulnerabilities.
How does a Linux VPS ensure high availability for hosting critical web apps?
A Linux VPS provides redundant infrastructure, automated backups, and load balancing options to maintain uptime and ensure your web applications remain accessible even during traffic spikes or hardware failures.
Can I customize the server environment on a Secure Linux VPS?
Yes, you have full root access to install, configure, and customize software, security settings, and application stacks according to your specific hosting requirements.
What support is available for managing a Secure Linux VPS?
We offer 24/7 technical support, comprehensive documentation, and managed services for monitoring, updates, and troubleshooting to help you maintain optimal performance and security.






Deja una respuesta