Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security

- Essential Criteria for Selecting Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security
- Comprehensive Guide to Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security
- Which firewall solutions with integrated IDS capabilities are currently considered the most secure for enterprise environments?
- How do modern firewall systems incorporate Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to enhance network security?
- What firewall architectures provide the strongest security when combined with IDS functionality?
- How do IDS rules function within a firewall's security framework to detect and prevent network threats?
- More information of interest
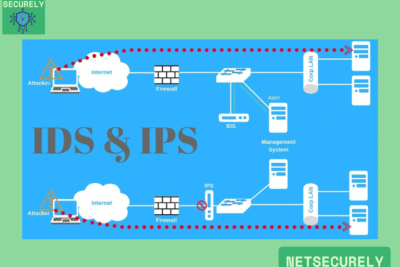
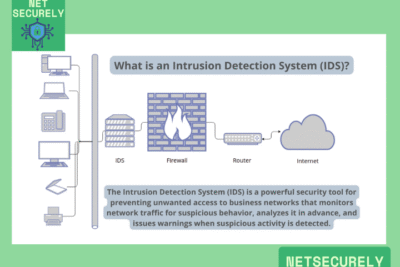
Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security, in today's complex digital landscape, organizations require advanced security measures to defend against evolving cyber threats. A critical component of any defense strategy involves deploying sophisticated network protection systems. Among the most effective solutions are those combining firewall capabilities with intrusion detection systems (IDS).

These integrated tools provide comprehensive monitoring, real-time threat analysis, and automated response mechanisms. This article explores the leading options available, focusing on the . We will examine key features, performance metrics, and deployment considerations to help you select the optimal solution for safeguarding your network infrastructure against modern security challenges.
You may be interested in reading : Best High-Speed VPNs for Optimal Web Performance
Essential Criteria for Selecting Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security
When evaluating Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security, key considerations include integration depth between firewall and IDS components, real-time threat detection capabilities, scalability for organizational growth, compliance with industry standards (e.g., NIST, GDPR), and total cost of ownership. These elements ensure the solution provides comprehensive protection against evolving cyber threats while maintaining operational efficiency.
Integration of Firewall and IDS Components
Effective integration between firewall and intrusion detection system (IDS) components is critical for seamless security operations. Unified management consoles, shared threat intelligence databases, and coordinated response mechanisms enable real-time blocking of malicious traffic. Solutions like Palo Alto Networks and FortiGate excel in this area by correlating firewall rules with IDS alerts to automatically mitigate threats without manual intervention.
Real-Time Threat Detection Capabilities
Top-tier firewalls with IDS employ advanced techniques such as deep packet inspection, behavioral analysis, and signature-based detection to identify threats in real time. These systems continuously monitor network traffic for anomalies, known attack patterns, and zero-day exploits, providing immediate alerts and automated responses to minimize potential damage.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
Scalability ensures the firewall-IDS solution can handle increasing network traffic and expanding infrastructure without degradation in performance. Key factors include throughput capacity, support for high-availability configurations, and modular licensing for additional features. Enterprise-grade options like Cisco Firepower and Check Point Quantum offer flexible scaling to accommodate growth while maintaining robust security.
Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
Adherence to regulatory frameworks (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS) is a fundamental requirement for organizations handling sensitive data. Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security often include built-in compliance reporting, audit trails, and predefined policy templates to simplify adherence. These features help organizations demonstrate due diligence and avoid penalties associated with non-compliance.
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Evaluating total cost of ownership involves assessing initial hardware/software costs, subscription fees for threat intelligence updates, maintenance expenses, and staffing requirements. While open-source solutions like pfSense may have lower upfront costs, commercial offerings typically provide comprehensive support and integrated features that reduce long-term operational burdens.
| Firewall Product | IDS Technology | Maximum Throughput | Key Feature |
| Palo Alto Networks | Advanced Threat Prevention | 10 Gbps | ML-Powered Threat Detection |
| FortiGate | FortiGuard AI Security | 20 Gbps | Integrated SD-WAN Support |
| Cisco Firepower | Snort-Based IDS | 15 Gbps | Threat Intelligence Integration |
| Check Point Quantum | ThreatCloud AI | 25 Gbps | Zero-Protection Architecture |
| pfSense | Suricata IDS | 5 Gbps | Open-Source Flexibility |
Comprehensive Guide to Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security
Which firewall solutions with integrated IDS capabilities are currently considered the most secure for enterprise environments?

Currently, enterprise environments seeking Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security should consider solutions such as Palo Alto Networks' Next-Generation Firewalls, which integrate advanced threat prevention including machine learning-based IDS/IPS, Cisco Firepower Threat Defense offering deep packet inspection and real-time intelligence, and Fortinet's FortiGate series with its custom security processor for high-performance intrusion detection; these platforms are distinguished by their comprehensive threat intelligence, automated response capabilities, and scalability to protect large networks against sophisticated cyber threats while ensuring minimal performance impact.
Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewalls
Palo Alto Networks delivers top-tier security through its Next-Generation Firewalls, which incorporate advanced IDS/IPS capabilities powered by machine learning and behavioral analytics to detect and block known and unknown threats in real-time; these firewalls utilize the App-ID and Threat-ID technologies to provide deep visibility and control over network traffic, ensuring that enterprises can defend against zero-day exploits, malware, and advanced persistent threats with high efficacy and minimal false positives, making them a preferred choice for organizations requiring stringent security compliance and robust network segmentation.
Cisco Firepower Threat Defense
Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) integrates intrusion detection and prevention with next-generation firewall functionalities, leveraging Snort-based rules and Cisco Talos intelligence for up-to-date threat protection; its strength lies in unified management via the Firepower Management Center, which allows for centralized policy enforcement, detailed analytics, and automated responses to security incidents, providing enterprises with a scalable solution that supports complex network architectures while maintaining high performance and reliability across distributed environments.
Fortinet FortiGate Series
Fortinet's FortiGate firewalls are renowned for their integrated IDS/IPS powered by FortiGuard Labs, offering continuous threat updates and leveraging custom security processors for accelerated inspection without compromising network speed; these solutions provide deep visibility into applications and users, support secure SD-WAN deployments, and include automated workflows for threat response, making them ideal for enterprises seeking a balance of high performance, cost-effectiveness, and comprehensive security in a single platform, especially for high-traffic networks.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Threat Intelligence | Real-time updates from FortiGuard Labs |
| Performance | Hardware-accelerated inspection with security processors |
| Management | Centralized via FortiManager for streamlined operations |
How do modern firewall systems incorporate Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to enhance network security?

Modern firewall systems integrate Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) through deep packet inspection (DPI), stateful analysis, and signature-based or anomaly-based detection mechanisms, enabling real-time monitoring and identification of malicious traffic patterns or policy violations. By combining traditional access control with behavioral analysis, these systems provide multi-layered defense, automatically alerting administrators or triggering predefined responses such as blocking suspicious IP addresses, thus significantly reducing the window of opportunity for attackers and fortifying network perimeters against evolving threats.
Integrated IDS Features in Next-Generation Firewalls
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) incorporate IDS functionalities by embedding deep packet inspection (DPI) and application-aware filtering, which go beyond port/protocol analysis to examine payload content for malicious signatures or behavioral anomalies. This integration allows for real-time detection of threats like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, or malware propagation, with automated responses such as connection termination or traffic logging. By unifying these capabilities, NGFWs reduce latency and complexity while providing comprehensive visibility into network traffic, ensuring that security policies are enforced dynamically and adaptively.
Automated Threat Response and Alert Mechanisms
Modern firewalls with integrated IDS employ automated response protocols to immediately counteract detected intrusions, such as blocking malicious IP addresses, quarantining affected devices, or modifying firewall rules in real-time. These systems utilize machine learning algorithms to reduce false positives and prioritize critical alerts, ensuring that security teams can focus on high-risk incidents. Additionally, they generate detailed logs and notifications through SIEM integration, enabling swift forensic analysis and compliance reporting, which strengthens overall network resilience against sophisticated attacks.
Comparative Analysis of Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security
When evaluating Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security, key differentiators include threat detection accuracy, performance impact, and management scalability. Leading solutions such as Palo Alto Networks, Cisco Firepower, and FortiGate offer advanced features like sandboxing, threat intelligence feeds, and customizable rule sets, which enhance their ability to identify and mitigate zero-day exploits and advanced persistent threats. The table below summarizes critical aspects of these platforms:
| Firewall Model | IDS Methodology | Key Features | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Palo Alto Networks | Signature & Anomaly-Based | WildFire Sandboxing, App-ID | Low Latency, High Throughput |
| Cisco Firepower | Network-Based IDS (NIDS) | Snort Integration, AMP | Moderate, Scalable |
| FortiGate | Deep Inspection & AI | FortiGuard Services, Fabric Integration | Optimized for Enterprises |
What firewall architectures provide the strongest security when combined with IDS functionality?
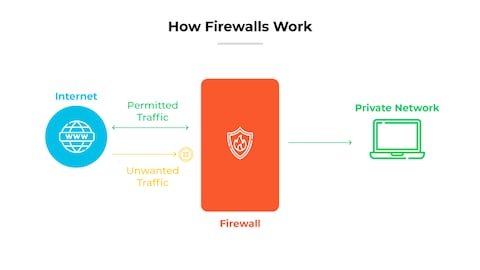
The most secure firewall architectures when integrated with IDS functionality are next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) with deep packet inspection (DPI), stateful multilayer inspection firewalls, and hybrid architectures combining network-based and host-based firewalls, as these systems provide comprehensive traffic analysis, application-layer filtering, and real-time threat correlation, with NGFWs offering the strongest security by merging traditional firewall rules, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and advanced threat intelligence feeds for a unified defense mechanism that constitutes the foundation of Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security.
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) with Integrated IDS/IPS
Next-generation firewalls represent the pinnacle of integrated security by combining traditional firewall capabilities with deep packet inspection (DPI), application awareness, and built-in intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS). These firewalls operate at Layer 7 of the OSI model, allowing them to inspect and control traffic based on applications and user identities rather than just ports and IP addresses. When IDS functionality is embedded, NGFWs can detect and block sophisticated threats like advanced persistent threats (APTs) and zero-day exploits in real-time, leveraging signature-based detection, anomaly-based heuristics, and behavioral analysis. The synergy between firewall policies and IDS alerts enables automated responses, such as dynamically updating rules to quarantine malicious hosts, making NGFWs exceptionally effective for modern network environments. Key features include:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Application Control | Blocks unauthorized apps and mitigates abuse |
| SSL/TLS Inspection | Decrypts and scans encrypted traffic for threats |
| Threat Intelligence Feeds | Updates defenses based on global threat data |
| User Identity Integration | Enforces policies based on users, not just devices |
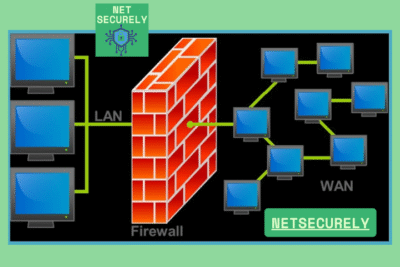
Stateful Multilayer Inspection Firewalls with External IDS
Stateful multilayer inspection firewalls provide robust security by examining packets across multiple OSI layers (e.g., network, transport, and application layers) while maintaining session state information. When paired with an external network-based IDS (NIDS), this architecture offers a defense-in-depth strategy: the firewall enforces access control and stateful rules, while the IDS monitors traffic for suspicious patterns or anomalies. The IDS can be deployed in promiscuous mode to analyze all traversing packets without impacting firewall performance, and it uses signature matching and statistical anomaly detection to identify threats like port scanning or malware propagation.
This combination allows for comprehensive coverage, with the firewall blocking unauthorized access and the IDS providing additional visibility and alerting for sophisticated attacks that might evade baseline firewall rules.
Hybrid Architectures: Network and Host-Based Solutions
Hybrid firewall-IDS architectures integrate network-based firewalls and host-based IDS (HIDS) to create a multi-layered security posture. Network firewalls (e.g., hardware or virtual appliances) control ingress and egress traffic at the perimeter, while HIDS agents on individual endpoints monitor system-level activities, such as file integrity changes, registry modifications, and process behaviors. This approach ensures that threats bypassing the network defenses are caught internally, providing visibility into east-west traffic and insider threats. The correlation of alerts from both network and host layers enables faster incident response, as security teams can cross-reference firewall logs with HIDS data to pinpoint compromised systems. This architecture is particularly effective in segmented networks, where micro-segmentation policies enforced by firewalls complement the detailed oversight of HIDS.
How do IDS rules function within a firewall's security framework to detect and prevent network threats?
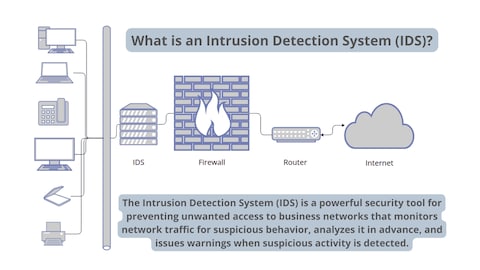
Intrusion Detection System (IDS) rules function within a firewall's security framework by analyzing network traffic against a predefined set of signatures or behavioral patterns to identify malicious activities, such as known attack signatures, protocol anomalies, or policy violations; when a rule is triggered, the system generates alerts or, in the case of an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), actively blocks the suspicious traffic, thereby enhancing threat detection and prevention capabilities by complementing the firewall’s stateful inspection with deeper packet analysis and heuristic-based monitoring.
Signature-Based Detection in IDS Rules
Signature-based detection in IDS rules operates by comparing network traffic against a database of known attack patterns, or signatures, which are predefined indicators of malicious activity such as specific byte sequences, strings, or packet structures; when a match is found, the system flags the traffic as a threat and can log, alert, or block it, depending on the configuration. This method is highly effective against well-documented threats like malware, exploits, or denial-of-service attacks but may struggle with zero-day vulnerabilities or polymorphic attacks that evade static signatures. For organizations seeking comprehensive protection, integrating these rules into Top Firewalls with IDS for Robust Security ensures that both known and emerging threats are mitigated through regularly updated signature databases and real-time analysis.
| Component | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Signature Database | Stores known threat patterns | SQL injection strings |
| Matching Engine | Compares traffic to signatures | Detects OR 1=1 in packets |
| Response Module | Executes actions on matches | Blocks IP or generates alert |
Anomaly-Based Detection Mechanisms
Anomaly-based detection mechanisms in IDS rules focus on identifying deviations from established baselines of normal network behavior, such as unusual traffic volumes, unexpected protocol usage, or atypical connection patterns, which may indicate novel or zero-day attacks; this approach uses statistical models, machine learning, or heuristic algorithms to dynamically adapt to network environments and flag outliers for further investigation. While it excels at detecting previously unknown threats or insider attacks, it can generate false positives if baselines are not accurately calibrated or during legitimate network changes. Deploying this within a firewall's security framework enhances proactive threat hunting and reduces reliance solely on signature updates.
| Component | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Behavioral Baseline | Defines normal network activity | Average bandwidth usage |
| Analysis Engine | Monitors for deviations | Spike in traffic at odd hours |
| Alert System | Notifies on anomalies | Flags port scanning activity |
Integration with Firewall Policies for Prevention
Integration with firewall policies enables IDS rules to transition from detection to prevention by automatically enforcing actions such as dropping packets, resetting connections, or blocking IP addresses when threats are identified, effectively combining deep packet inspection with access control measures to create a dynamic defense layer. This synergy allows firewalls to not only filter traffic based on rules like ports and IPs but also respond intelligently to content-based threats, reducing the window of exposure and minimizing manual intervention. For optimal performance, rules must be finely tuned to balance security and network functionality, avoiding unnecessary disruptions while maintaining robust protection.
| Integration Aspect | Benefit | Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Blocking | Immediate threat mitigation | Drops packets from malicious IP |
| Policy Synchronization | Cohesive security posture | Aligns IDS alerts with firewall ACLs |
| Log Correlation | Enhanced forensic analysis | Combines firewall and IDS logs for incidents |
More information of interest
What are the key features to look for in a firewall with IDS for robust security?
When evaluating a firewall with Intrusion Detection System (IDS), prioritize features such as real-time monitoring, signature-based and anomaly-based detection, automated threat response, and integration with existing security infrastructure for comprehensive network protection.
How does an IDS enhance the capabilities of a traditional firewall?
An IDS enhances a traditional firewall by providing deep packet inspection, identifying suspicious activities or patterns that evade standard firewall rules, and offering threat intelligence to detect and respond to advanced threats, thereby strengthening overall security posture.
Which top firewalls with IDS are recommended for enterprise-level security?
Leading enterprise-grade firewalls with integrated IDS include Palo Alto Networks with its advanced threat prevention, Cisco Firepower offering robust intrusion detection, Fortinet FortiGate with its AI-driven security, and Check Point solutions known for their comprehensive threat mitigation.
What are the common challenges when deploying a firewall with IDS?
Common challenges include managing false positives, ensuring system performance isn't degraded by intensive monitoring, maintaining regular updates for threat signatures, and configuring the system to align with specific organizational security policies without creating vulnerabilities.



Deja una respuesta